In the field of audio recording and amplification, microphone directivity is a key factor influencing sound capture quality. Omnidirectional and cardioid microphones are the two most common types of directivity, and they differ significantly in terms of working principle, pickup range, suitable applications, and sound quality. This article will explore the fundamental principles of microphones and provide a detailed analysis of the differences between omnidirectional and cardioid microphones to help you choose the right device for your needs.
The core function of a microphone is to convert sound waves into electrical signals. A microphone's basic structure includes a diaphragm that vibrates when sound waves hit it, thereby generating an electrical signal in the internal coil (or capacitor) of the microphone.
Microphone directivity (or polar pattern) refers to the microphone's sensitivity to sound from different directions. Based on pickup patterns, microphones are generally categorized into the following types:
Omnidirectional and cardioid microphones are the most widely used types. Below is a detailed explanation of their characteristics and differences.
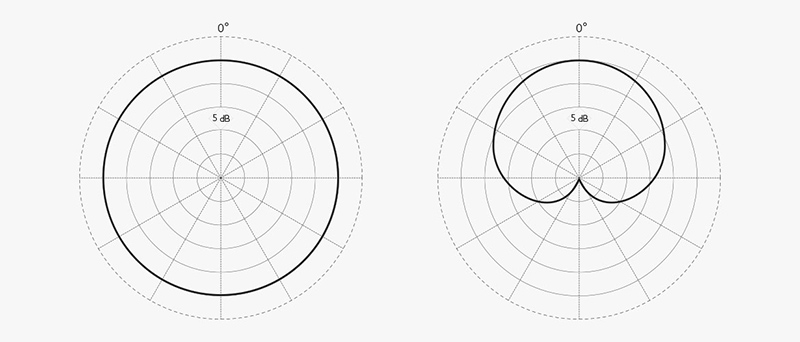
An omnidirectional microphone has equal sensitivity to sound from all directions, forming a spherical pickup pattern. This means that the microphone will capture sound evenly, regardless of the direction from which it comes.
Principle:
The diaphragm of an omnidirectional microphone is not sensitive to the direction of incoming sound waves. It typically uses a pressure-sensitive mechanism or diaphragm design to achieve balanced sound pickup from all directions.

A cardioid microphone has the highest sensitivity at the front, reduced sensitivity at the sides, and the lowest sensitivity at the back. Its pickup pattern resembles a heart shape, hence the name "cardioid microphone."
Principle:

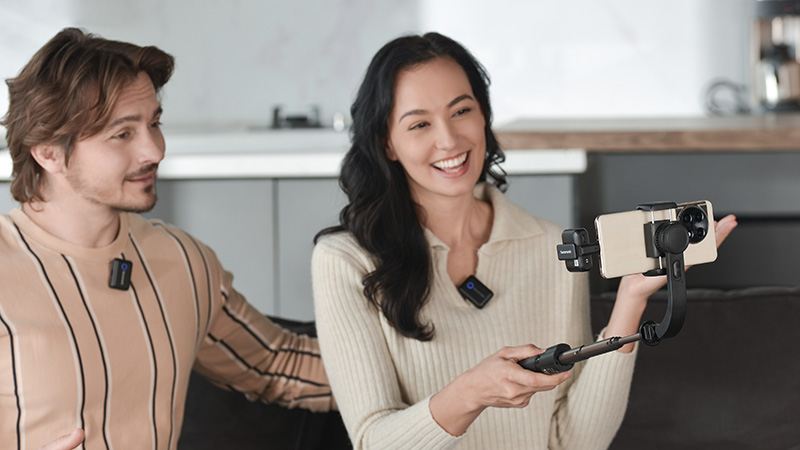
When choosing a microphone, you should consider the recording environment, pickup needs, and sound characteristics:

Omnidirectional and cardioid microphones each have their advantages and are suited for different scenarios. Omnidirectional microphones excel in capturing natural sound and spatial awareness but are prone to picking up ambient noise. In contrast, cardioid microphones are ideal for isolating the main sound source and reducing background noise, but they require precise positioning.
In practical applications, it’s important to choose the right microphone based on your recording environment and goals. For interviews, meetings, or ambient sound capture, an omnidirectional microphone is often the better choice. For live streaming, stage performances, and vocal recording, a cardioid microphone will deliver better clarity and focus. By understanding the characteristics and differences between these two types of microphones, you can better "master the sound" and achieve optimal recording results.